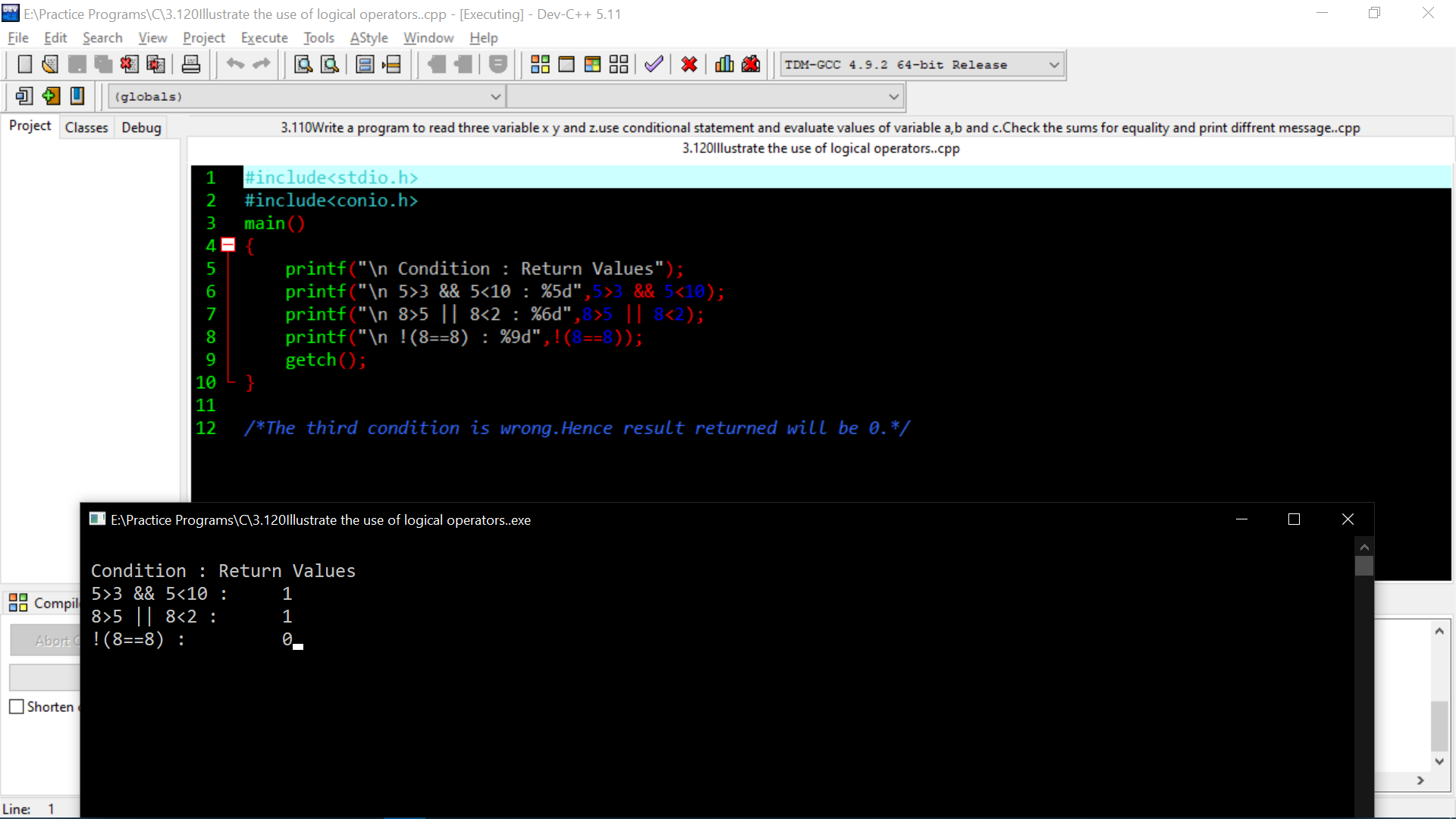
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | #include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>main(){ printf("\n Condition : Return Values"); printf("\n 5>3 && 5<10 : %5d",5>3 && 5<10); printf("\n 8>5 || 8<2 : %6d",8>5 || 8<2); printf("\n !(8==8) : %9d",!(8==8)); getch();}/*The third condition is wrong.Hence result returned will be 0.*/ |
The logical operators are used to evaluate the conditions in an expression and make decisions based on the result. There are three logical operators in C programming language:
- && (AND) operator: It evaluates to true if both the conditions are true.
- || (OR) operator: It evaluates to true if either of the conditions are true.
- ! (NOT) operator: It inverts the truth value of an expression.
This above program demonstrates the use of logical operators in C. The logical operators used in this program are && (AND), || (OR), and ! (NOT).
The first condition, 5 > 3 && 5 < 10, returns 1 as the result. This is because both of the conditions are true, and the AND operator returns true only if both conditions are true.
The second condition, 8 > 5 || 8 < 2, returns 1 as the result. This is because at least one of the conditions is true, and the OR operator returns true if either of the conditions is true.
The third condition, !(8 == 8), returns 0 as the result. This is because the NOT operator negates the expression within the parenthesis. The expression 8 == 8 is true, so negating it returns false.
The results of these conditions are printed on the screen using the printf function.
Thanks